2.1 Understanding Zuoying Armed Forces General Hospital
2.1.1 Organizational Overview
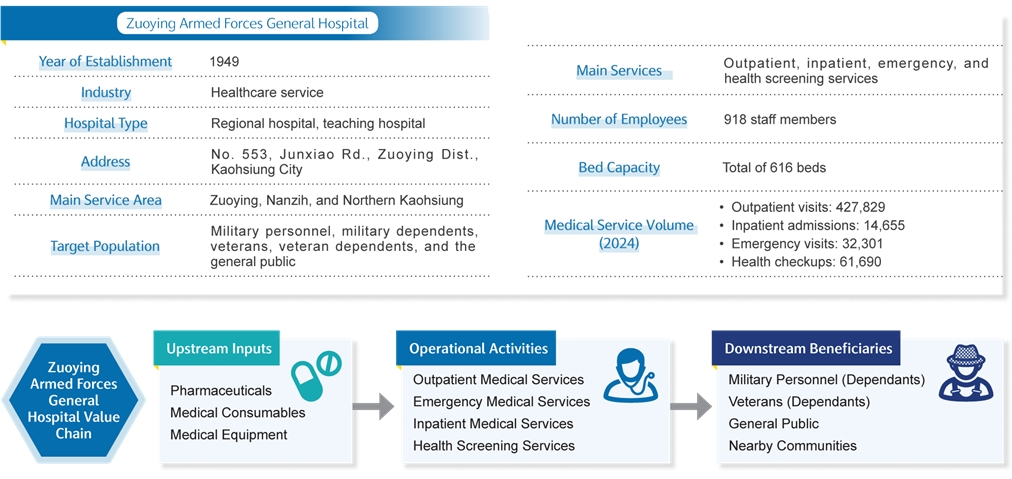
The predecessor of Zuoying Armed Forces General Hospital dates back to the Japanese colonial period, when it was established as the ‘Naval Temporary Clinic’. After retrocession of Taiwan in 1945, it was reorganized as ‘Naval Hospital’. Following several policy-driven name changes over the years, it was officially renamed the ‘Zuoying Armed Forces General Hospital’ on November 1, 2023. Our hospital not only bears the responsibility of safeguarding the health of military personnel and their dependents but also undertakes medical research in support of national defense and military needs. At the same time, it offers medical services to the general public. Upholding our core values of ‘Loyalty and Responsibility, Treating Patients as Family’, we are dedicated to providing high-quality healthcare to both military and civilian populations. Meanwhile, we continue to pursue our vision of ‘becoming medical stronghold for naval military medicine and a trusted healthcare resource for the community’s military and civilians’.
Operational Performance
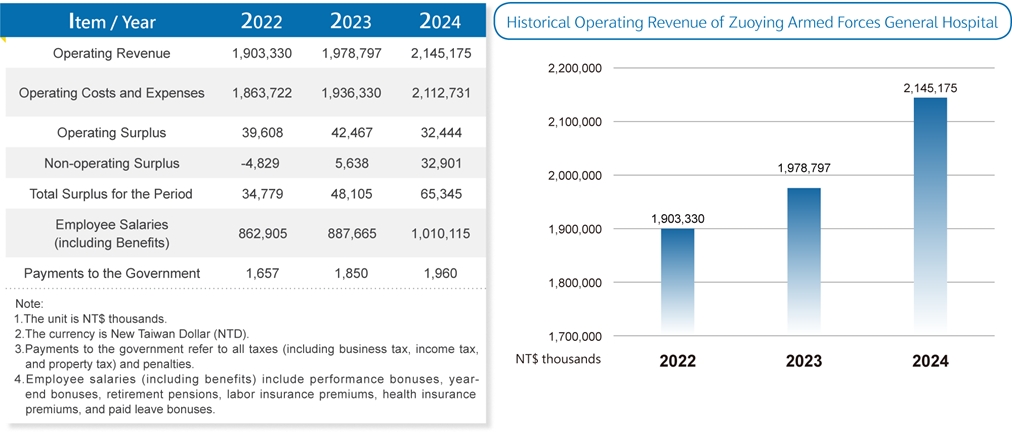
Zuoying Armed Forces General Hospital is committed to delivering high-quality medical services, achieving a total of 427,829 outpatient visits, 14,655 inpatient admissions, 32,301 emergency visits, and 61,690 health checkups in 2024. The hospital’s operating revenue surpassed NT$2 billion, further supported by over NT$600 million in subsidies from the Ministry of National Defense.
Operation Management Governance Composition and Structure
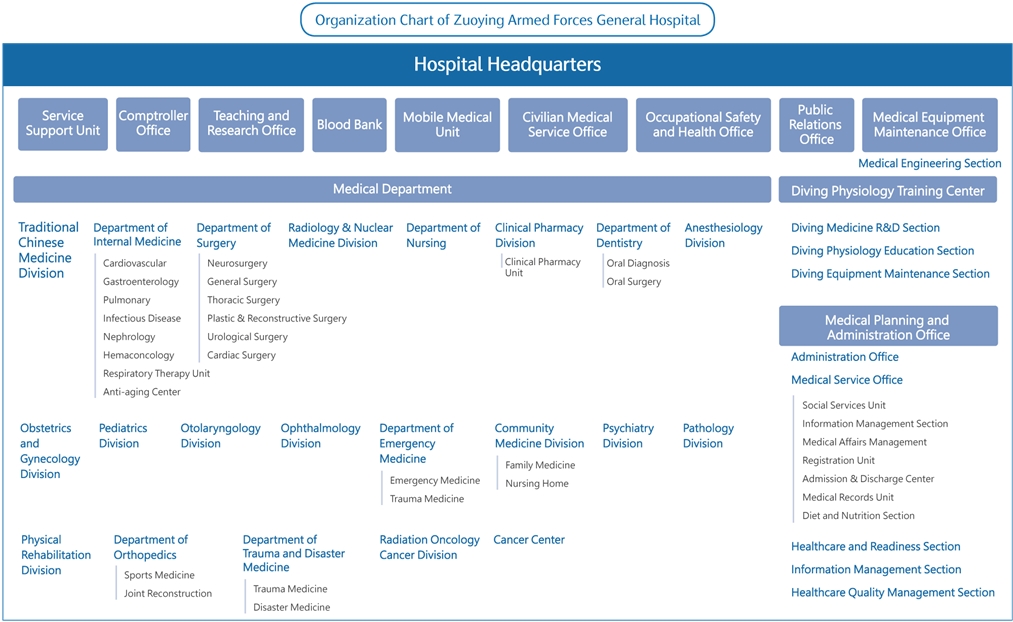
Zuoying Armed Forces General Hospital is one of the 14 military hospitals, including 6 general hospitals and 8 branch hospitals, that are under jurisdiction of the Medical Affairs Bureau, Ministry of National Defense. The hospital’s Superintendent (Major General) and Deputy Superintendent (Colonel) are appointed by the Medical Affairs Bureau in accordance with relevant regulations. The Superintendent serves as the highest level of governance within the hospital, responsible for overall leadership and strategic decision-making. Together with the Deputy Superintendent and the Director of the Civilian Medical Services Department, the leadership team guides both administrative and clinical departments, coordinating hospital operations and management to ensure the quality and efficiency of healthcare services.
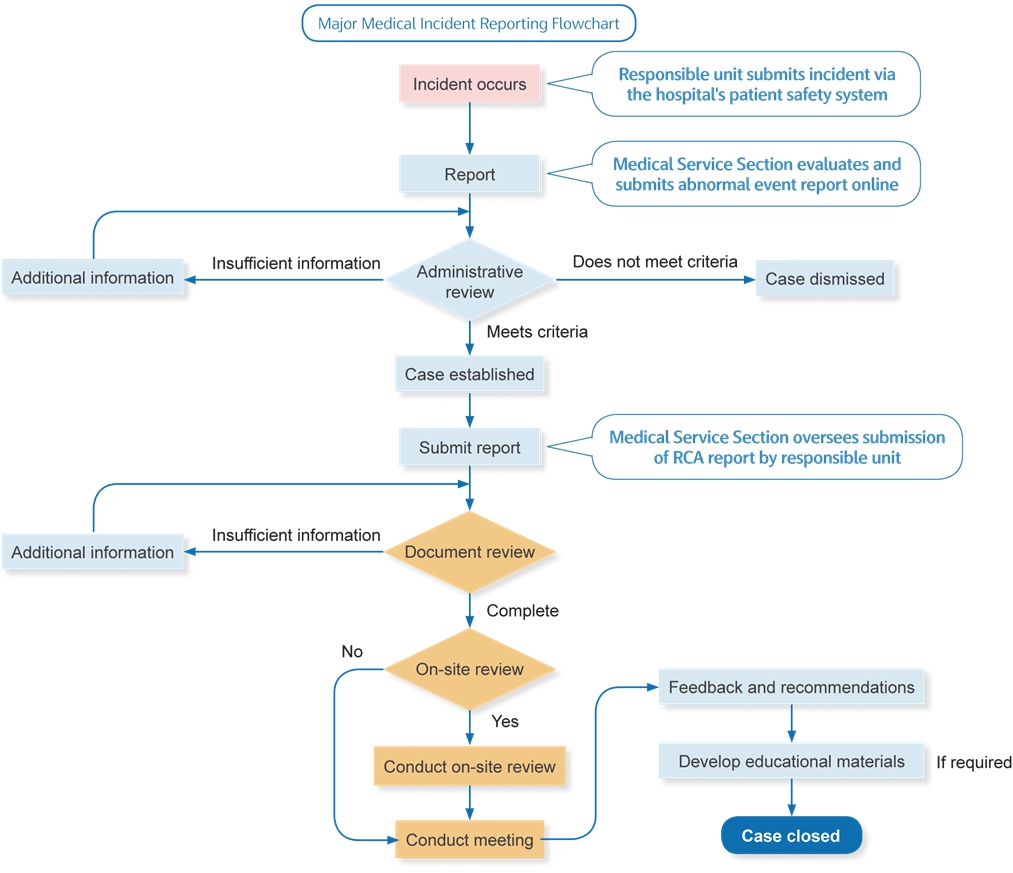
Major Incident Reporting Mechanism
The hospital adopts a strict hierarchical reporting system for major incidents. Such events are reported promptly to the Superintendent and Deputy Superintendent through meetings or official internal memos. Major incidents are defined as critical events that significantly impact institutional operations, national defense security, military discipline, medical system functionality, or public trust.
For staff and patient safety incidents, the definitions are as follows:
- Staff safety incidents: Cases that require the convening of a disciplinary or personnel review committee.
- Patient safety incidents: In accordance with the ‘Regulations on the Reporting and Handling of Major Medical Incidents’, five types of serious patient safety events must be reported, including surgical or invasive procedure errors, blood transfusions with incompatible blood types, prescription errors, misuse of medical equipment, etc.